为什么异常处理选择中间件?
传统的ASP.NET可以采用异常过滤器的方式处理异常,在ASP.NET CORE中,是以多个中间件连接而成的管道形式处理请求的,不过常用的五大过滤器得以保留,同样可以采用异常过滤器处理异常,但是异常过滤器不能处理MVC中间件以外的异常,为了全局统一考虑,采用中间件处理异常更为合适
为什么选择自定义异常中间件?
先来看看ASP.NET CORE 内置的三个异常处理中间件 DeveloperExceptionPageMiddleware, ExceptionHandlerMiddleware,StatusCodePagesMiddleware
1.DeveloperExceptionPageMiddleware
能给出详细的请求/返回/错误信息,因为包含敏感信息,所以仅适合开发环境
2.ExceptionHandlerMiddleware
仅处理500错误
3.StatusCodePagesMiddleware
能处理400-599之间的错误,但需要Response中不能包含内容(ContentLength=0 && ContentType=null,经实验不能响应mvc里未捕获异常)
由于ExceptionHandlerMiddleware和StatusCodePagesMiddleware的各自的限制条件,两者需要搭配使用。相比之下自定义中间件更加灵活,既能对各种错误状态进行统一处理,也能按照配置决定处理方式。
CustomExceptionMiddleWare
首先声明异常中间件的配置类
/// <summary> /// 异常中间件配置对象 /// </summary> public class CustomExceptionMiddleWareOption { public CustomExceptionMiddleWareOption( CustomExceptionHandleType handleType = CustomExceptionHandleType.JsonHandle, IList<PathString> jsonHandleUrlKeys = null, string errorHandingPath = "") { HandleType = handleType; JsonHandleUrlKeys = jsonHandleUrlKeys; ErrorHandingPath = errorHandingPath; } /// <summary> /// 异常处理方式 /// </summary> public CustomExceptionHandleType HandleType { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Json处理方式的Url关键字 /// <para>仅HandleType=Both时生效</para> /// </summary> public IList<PathString> JsonHandleUrlKeys { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 错误跳转页面 /// </summary> public PathString ErrorHandingPath { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// 错误处理方式 /// </summary> public enum CustomExceptionHandleType { JsonHandle = 0, //Json形式处理 PageHandle = 1, //跳转网页处理 Both = 2 //根据Url关键字自动处理 } 声明异常中间件的成员
/// <summary> /// 管道请求委托 /// </summary> private RequestDelegate _next; /// <summary> /// 配置对象 /// </summary> private CustomExceptionMiddleWareOption _option; /// <summary> /// 需要处理的状态码字典 /// </summary> private IDictionary<int, string> exceptionStatusCodeDic; public CustomExceptionMiddleWare(RequestDelegate next, CustomExceptionMiddleWareOption option) { _next = next; _option = option; exceptionStatusCodeDic = new Dictionary<int, string> { { 401, "未授权的请求" }, { 404, "找不到该页面" }, { 403, "访问被拒绝" }, { 500, "服务器发生意外的错误" } //其余状态自行扩展 }; } 异常中间件主要逻辑
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { Exception exception = null; try { await _next(context); //调用管道执行下一个中间件 } catch (Exception ex) { context.Response.Clear(); context.Response.StatusCode = 500; //发生未捕获的异常,手动设置状态码 exception = ex; } finally { if (exceptionStatusCodeDic.ContainsKey(context.Response.StatusCode) && !context.Items.ContainsKey("ExceptionHandled")) //预处理标记 { var errorMsg = string.Empty; if (context.Response.StatusCode == 500 && exception != null) { errorMsg = $"{exceptionStatusCodeDic[context.Response.StatusCode]}/r/n{(exception.InnerException != null ? exception.InnerException.Message : exception.Message)}"; } else { errorMsg = exceptionStatusCodeDic[context.Response.StatusCode]; } exception = new Exception(errorMsg); } if (exception != null) { var handleType = _option.HandleType; if (handleType == CustomExceptionHandleType.Both) //根据Url关键字决定异常处理方式 { var requestPath = context.Request.Path; handleType = _option.JsonHandleUrlKeys != null && _option.JsonHandleUrlKeys.Count( k => context.Request.Path.StartsWithSegments(k, StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase)) > 0 ? CustomExceptionHandleType.JsonHandle : CustomExceptionHandleType.PageHandle; } if (handleType == CustomExceptionHandleType.JsonHandle) await JsonHandle(context, exception); else await PageHandle(context, exception, _option.ErrorHandingPath); } } } /// <summary> /// 统一格式响应类 /// </summary> /// <param name="ex"></param> /// <returns></returns> private ApiResponse GetApiResponse(Exception ex) { return new ApiResponse() { IsSuccess = false, Message = ex.Message }; } /// <summary> /// 处理方式:返回Json格式 /// </summary> /// <param name="context"></param> /// <param name="ex"></param> /// <returns></returns> private async Task JsonHandle(HttpContext context, Exception ex) { var apiResponse = GetApiResponse(ex); var serialzeStr = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(apiResponse); context.Response.ContentType = "application/json"; await context.Response.WriteAsync(serialzeStr, Encoding.UTF8); } /// <summary> /// 处理方式:跳转网页 /// </summary> /// <param name="context"></param> /// <param name="ex"></param> /// <param name="path"></param> /// <returns></returns> private async Task PageHandle(HttpContext context, Exception ex, PathString path) { context.Items.Add("Exception", ex); var originPath = context.Request.Path; context.Request.Path = path; //设置请求页面为错误跳转页面 try { await _next(context); } catch { } finally { context.Request.Path = originPath; //恢复原始请求页面 } } 使用扩展类进行中间件注册
public static class CustomExceptionMiddleWareExtensions { public static IApplicationBuilder UseCustomException(this IApplicationBuilder app, CustomExceptionMiddleWareOption option) { return app.UseMiddleware<CustomExceptionMiddleWare>(option); } } 在Startup.cs的Configuref方法中注册异常中间件
app.UseCustomException(new CustomExceptionMiddleWareOption( handleType: CustomExceptionHandleType.Both, //根据url关键字决定处理方式 jsonHandleUrlKeys: new PathString[] { "/api" }, errorHandingPath: "/home/error")); 接下来我们来进行测试,首先模拟一个将会进行页面跳转的未经捕获的异常
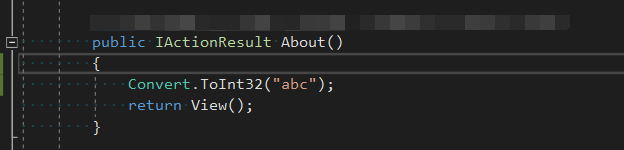
访问/home/about的结果
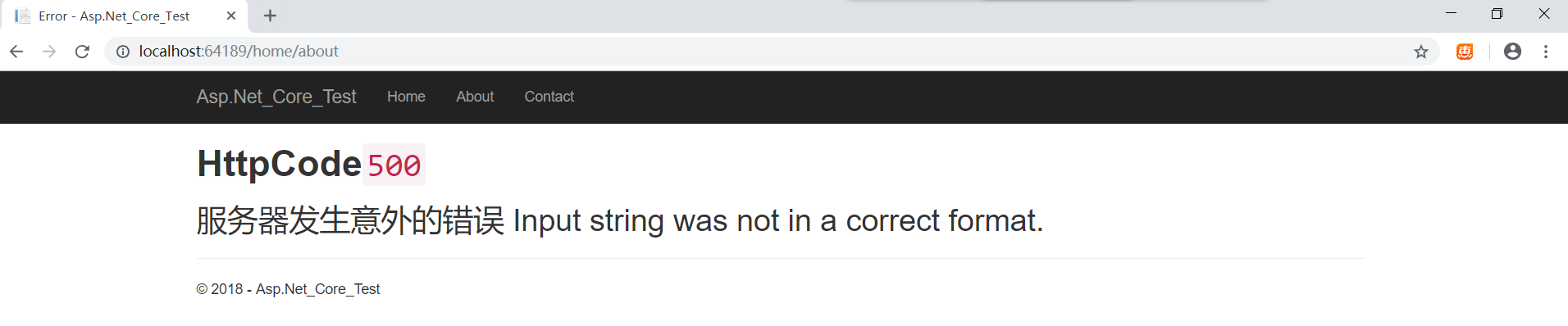
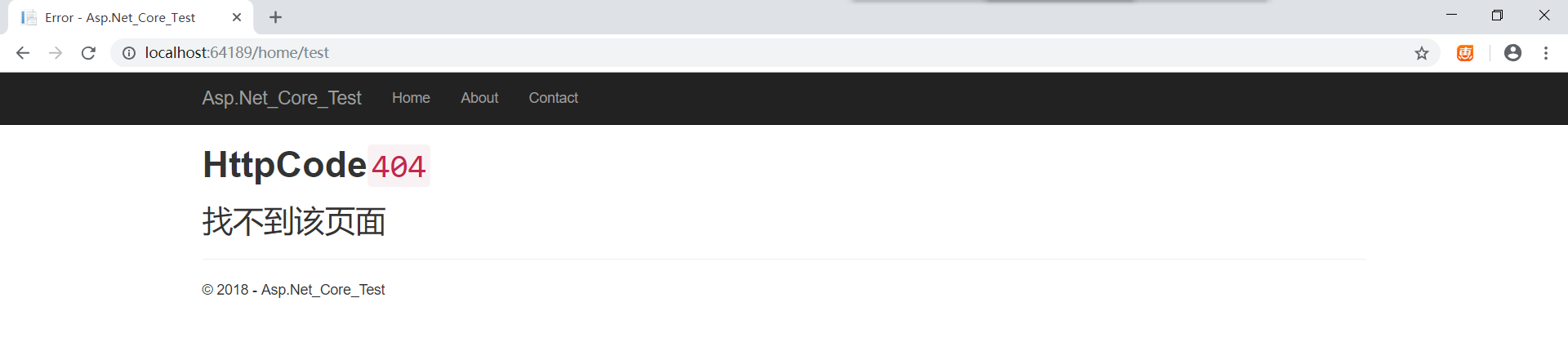
访问/home/test的结果 (该地址不存在)
OK异常跳转页面的方式测试完成,接下来我们测试返回统一格式(json)的异常处理,同样先模拟一个未经捕获的异常
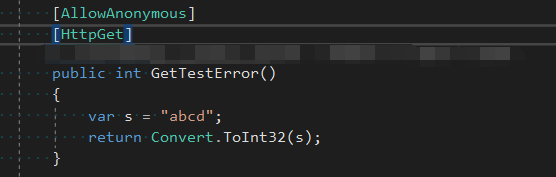
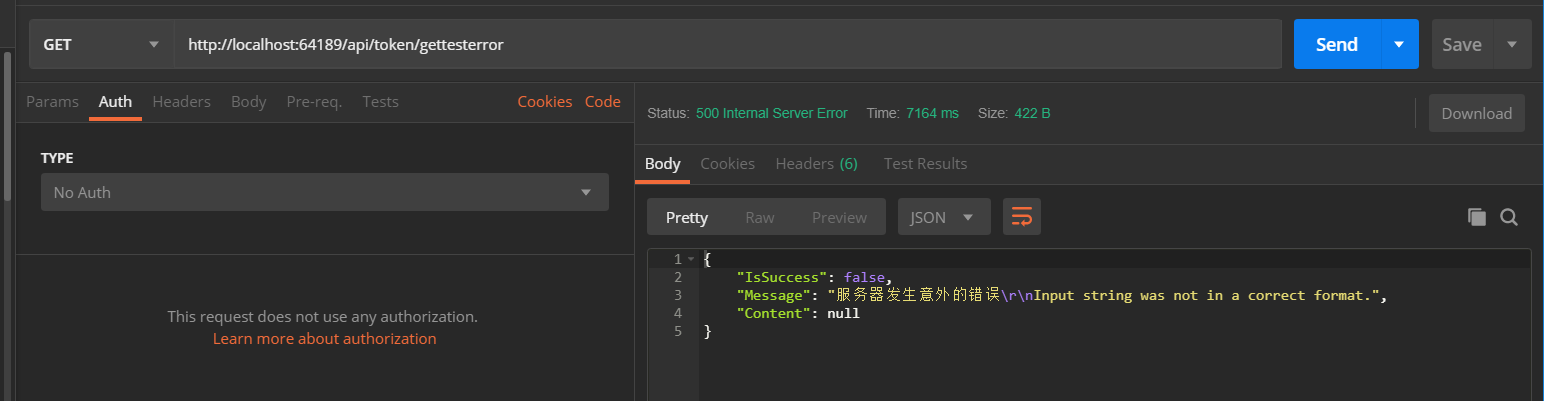
访问/api/token/gettesterror的结果
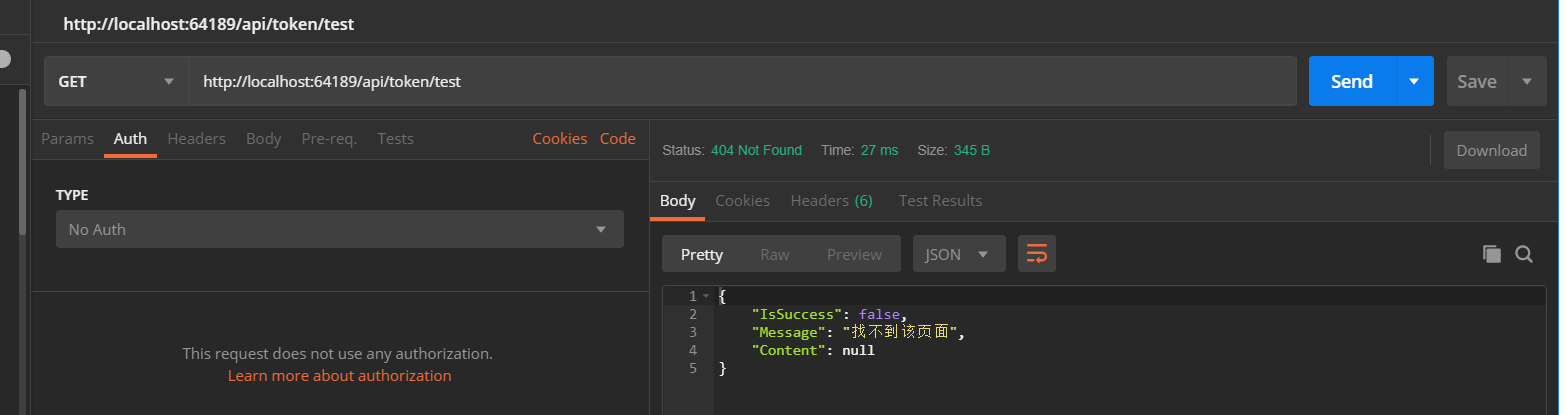
访问/api/token/test的结果 (该地址不存在)
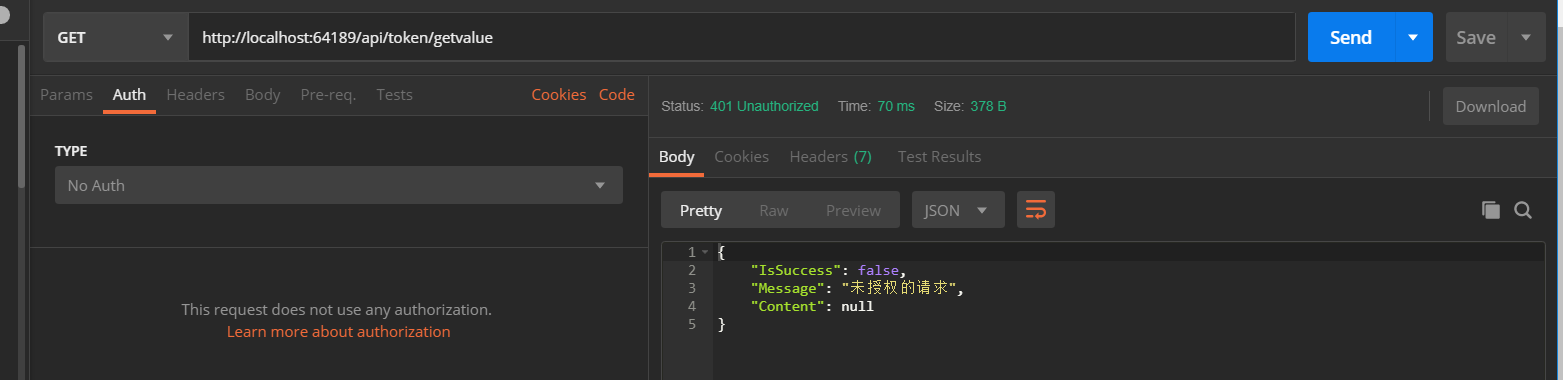
访问/api/token/getvalue的结果 (该接口需要身份验证)
测试完成,页面跳转和统一格式返回都没有问题,自定义异常中间件已按预期工作
需要注意的是,自定义中间件会响应每个HTTP请求,所以处理逻辑一定要精简,防止发生不必要的性能问题
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对CuoXin错新网的支持。
注:相关教程知识阅读请移步到ASP.NET教程频道。